| Literature link | GPT Summary | Evidence category | Disease type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 17851799 | This study evaluated the prevalence and predictive value of traditional risk factors for gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) in Caucasian women. Analyzing data from 1,414 GDM cases and 1,011 healthy pregnant women, significant differences were found in age, BMI, prior macrosomia, prior GDM, and family history of diabetes between groups. Cut-off values were 28 years for age and 23 kg/m2 for BMI. Accumulation of two or more risk factors was common in GDM but not in healthy women. Prior GDM (OR: 4.35) and family history of diabetes (OR: 3.03) were the strongest predictors, followed by age, BMI, and prior macrosomia. Multiple logistic regression showed significant interactions (OR: 3.19; sensitivity: 57.9%, specificity: 69.8%). Traditional risk factor-based selective screening had relatively low sensitivity, identifying less than 60% of at-risk women, with a lower BMI cut-off suggested for GDM screening. | Risk factor | GDM |
| 21268030 | This study aimed to develop a predictive model for gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) using maternal characteristics and biochemical markers at 11-13 weeks' gestation. From a prospective screening of 11,464 pregnancies, including 297 GDM cases, significant predictors were identified: maternal age, BMI, racial origin, previous GDM, and macrosomic neonate history. A case-control study measuring adiponectin, FSTL3, and SHBG showed lower adiponectin and SHBG levels in GDM cases compared to controls (p < 0.05), with no significant difference in FSTL3. Using maternal characteristics alone, the detection rate for GDM was 61.6% at a 20% false-positive rate, which improved to 74.1% by incorporating adiponectin and SHBG. Thus, first-trimester screening combining maternal characteristics and biomarkers can effectively predict GDM. | Risk factor | GDM |
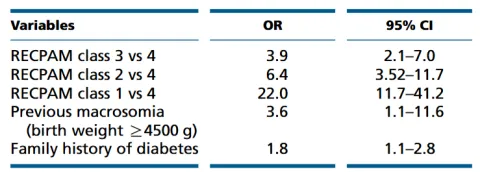
| 24114434 | This study evaluated the predictive value of selective screening (SS) risk factors (RFs) for gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) and aimed to identify high-risk subgroups using the RECPAM method. Among 1015 women screened, 113 (11.1%) were diagnosed with GDM. SS criteria missed 23% of GDM cases due to absence of RFs. RECPAM identified fasting plasma glucose >5.1 mmol/L and pre-pregnancy BMI as significant predictors. Including previous macrosomia and family history of diabetes in a logistic model further enhanced prediction accuracy. The RECPAM-based approach could halve undiagnosed GDM cases but requires more oral glucose tolerance tests. | Risk factor | GDM |
Figure's link
RF's name
Previous Macrosomia
RF's type
medical history