| Literature link | GPT Summary | Evidence category | Disease type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20876721 | This study aimed to explore predictors of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) by integrating both simple maternal measures and novel biomarkers to determine how effectively GDM can be predicted in the first trimester. The research involved 124 women who developed GDM and 248 control subjects, with data collected on factors such as age, BMI, parity, race, smoking, prior GDM, family history of diabetes, and blood pressure. Blood samples were analyzed for both routine (lipids, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, and γ-glutamyltransferase) and novel biomarkers (adiponectin, E-selectin, and tissue plasminogen activator [t-PA]). Stepwise regression identified elevated t-PA and low HDL cholesterol as independent predictors of GDM beyond basic maternal factors. Incorporating these biomarkers improved the area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve (AUC-ROC) from 0.824 to 0.861 and the integrated discrimination improvement (IDI) by 0.052, suggesting that GDM prediction can be enhanced by including specific blood measures like lipids and t-PA alongside simple clinical data. |
Risk factor |
GDM |
| 32757408 | This study highlights that first-trimester prognostic models for GDM, which include BMI ≥30 kg/m2 as a critical risk factor, outperform the single risk factor approach. The inclusion of BMI significantly enhances model accuracy, with c-statistics improving from 0.74-0.78 to 0.78-0.80 upon adding glucose measurements, compared to 0.72 for the single risk factor method 19. BMI's role is underscored as a vital component in these models for effective GDM screening |
Risk factor |
GDM |
| 27576867 | In this external validation, prognostic models for gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) that included maternal body mass index (BMI) demonstrated superior discrimination, with C statistics up to 0.78. BMI was a key predictor in the top four models, which also comprised factors like maternal age and history of GDM. These models showed good calibration and positive net benefit, underlining BMI's critical role in effectively predicting GDM risk during early pregnancy | Risk factor | GDM |
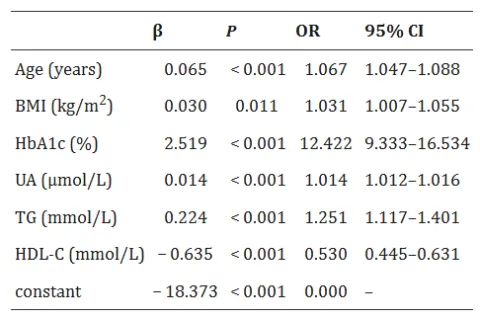
| 38085430 | In this study, pre-pregnancy Body Mass Index (BMI) was identified as an independent risk factor for gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), alongside age, HbA1c, uric acid, triglycerides, and HDL cholesterol. The developed prediction model, incorporating BMI among other factors, showed good discrimination with an AUC of 0.803 in the modeling cohort and 0.782 in the validation cohort. This highlights BMI's critical role in early GDM risk assessment, facilitating targeted monitoring and intervention for high-risk pregnant women | Risk factor | GDM |
Figure's link
RF's name
Pregestational Body Mass Index
RF's type
demographics