| Literature link | GPT Summary | Evidence category | Disease type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 33042010 | This study aimed to explore predictors of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) by integrating both simple maternal measures and novel biomarkers to determine how effectively GDM can be predicted in the first trimester. The research involved 124 women who developed GDM and 248 control subjects, with data collected on factors such as age, BMI, parity, race, smoking, prior GDM, family history of diabetes, and blood pressure. Blood samples were analyzed for both routine (lipids, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, and γ-glutamyltransferase) and novel biomarkers (adiponectin, E-selectin, and tissue plasminogen activator [t-PA]). Stepwise regression identified elevated t-PA and low HDL cholesterol as independent predictors of GDM beyond basic maternal factors. Incorporating these biomarkers improved the area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve (AUC-ROC) from 0.824 to 0.861 and the integrated discrimination improvement (IDI) by 0.052, suggesting that GDM prediction can be enhanced by including specific blood measures like lipids and t-PA alongside simple clinical data. |
Risk factor |
GDM |
| 20876721 | This study aimed to explore predictors of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) by integrating both simple maternal measures and novel biomarkers to determine how effectively GDM can be predicted in the first trimester. The research involved 124 women who developed GDM and 248 control subjects, with data collected on factors such as age, BMI, parity, race, smoking, prior GDM, family history of diabetes, and blood pressure. Blood samples were analyzed for both routine (lipids, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, and γ-glutamyltransferase) and novel biomarkers (adiponectin, E-selectin, and tissue plasminogen activator [t-PA]). Stepwise regression identified elevated t-PA and low HDL cholesterol as independent predictors of GDM beyond basic maternal factors. Incorporating these biomarkers improved the area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve (AUC-ROC) from 0.824 to 0.861 and the integrated discrimination improvement (IDI) by 0.052, suggesting that GDM prediction can be enhanced by including specific blood measures like lipids and t-PA alongside simple clinical data. |
Risk factor |
GDM |
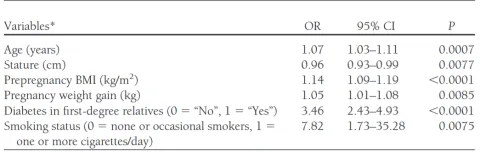
| 11978679 | This study highlights the critical role of maternal age in gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) and gestational impaired glucose tolerance (GIGT). Through a prospective case-control design involving 85 women with GDM, 63 with GIGT, and 125 controls, it was found that age is an independent risk factor for both conditions. Specifically, women diagnosed with GDM and GIGT had significantly higher mean ages compared to those with normal glucose tolerance. The analysis revealed that as maternal age increases, so does the likelihood of developing GDM or GIGT, even after adjusting for other variables such as pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI), weight gain during pregnancy, family history of diabetes, irregular menses, history of spontaneous abortion, educational level, and vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC). While these additional factors contribute to the overall risk profile, age stands out as a pivotal element demanding special attention. Consequently, this underscores the necessity for closer monitoring and early intervention strategies specifically tailored for older pregnant women to mitigate the risks associated with GDM and GIGT. | Risk factor | GDM |
Figure's link
RF's name
Age
RF's type
demographics