| Literature link | GPT Summary | Evidence category | Disease type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 39369463 | This study evaluates the antiviral effects and underlying mechanisms of electroacupuncture combined with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TF) in treating chronic hepatitis B (CHB). Using an HBV-infected mouse model, the combination therapy (E_T) demonstrated a greater reduction in serum HBV DNA (2.2 log10 IU/mL) compared to TF alone (1.98 log10 IU/mL), with superior inhibition of HBeAg and HBsAg levels. Multi-omics analysis revealed that E_T modulates the PPAR pathway, upregulates taurine and all-trans-retinoic acid, and enhances gut microbiota composition, contributing to improved intestinal barrier integrity. Mechanistically, E_T inhibited the PGC-1α/PPAR-α/SIRT1 pathway while activating JAK/STAT signaling through IFN-γ, p-JAK1, p-JAK2, and p-STAT1, leading to immune modulation and enhanced antiviral effects. These findings suggest that E_T, through its regulation of metabolic and immune pathways, may serve as a promising adjuvant therapy for CHB, particularly in achieving a functional cure. |
Mechanism |
Hepatitis B virus |
| 20430009 | Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection remains a clinical challenge despite the use of nucleoside analogues and interferon-alpha. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), which are involved in glucose and lipid metabolism, immune reactions, and inflammation, were studied for their potential role in suppressing HBV replication. In vitro experiments using HepG2 cells transfected with the HBV genome demonstrated that while the PPARalpha ligand bezafibrate had no effect on HBV replication, the PPARgamma ligand rosiglitazone significantly reduced HBV DNA, hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), and hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) in the culture supernatant. Southern blot analysis confirmed that rosiglitazone inhibited the replicative intermediates of HBV. The suppressive effect of rosiglitazone was blocked by GW9662, a PPARgamma antagonist. Additionally, rosiglitazone showed a synergistic effect with lamivudine or interferon-alpha-2b in inhibiting HBV replication. This study suggests that rosiglitazone, in combination with nucleoside analogues or interferon, could be a promising therapeutic strategy for chronic HBV infection. | Mechanism | Hepatitis B virus |
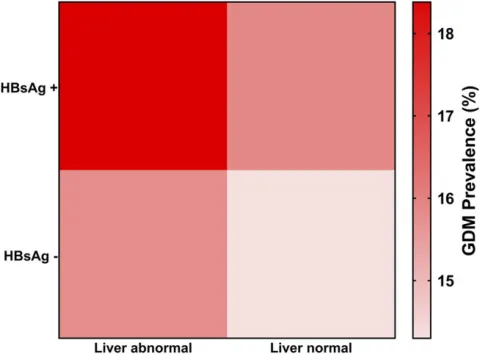
| 35899024 | The study investigates the link between HBV infection, liver function, and the risk of developing GDM among a large cohort of pregnant women in the Xiamen area. It uses big data from maternal and child health records over a decade to model the impact of HBV and liver function on GDM through logistic regression. Results indicate that HBsAg positivity is significantly associated with GDM, independent of liver function status, highlighting the importance of considering HBV infection when assessing GDM risk. | Risk factor | GDM |
RF's name
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
RF's type
Hepatitis B indicator