| Literature link | GPT Summary | Evidence category | Disease type |
|---|---|---|---|
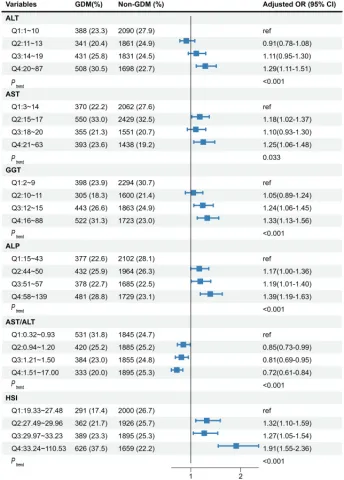
| 38836232 | This study aimed to investigate the relationship between maternal liver biomarkers and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), as well as the potential causality and interactions between liver biomarkers and lipid levels on GDM risk. Data were obtained from the ongoing Zhoushan Pregnant Women Cohort, which included 9,148 pregnant women. Liver function tests, including ALT, AST, GGT, ALP, and hepatic steatosis index, were measured in early pregnancy, and GDM screening was completed. The results revealed that the highest quartile of liver function index (LFI) was significantly associated with an increased risk of GDM, with odds ratios (OR) ranging from 1.29 to 3.15, particularly in relation to abnormal postprandial blood glucose levels. Additionally, Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis confirmed a causal link between ALT levels and GDM (OR = 1.28, 95% CI: 1.05-1.54). Furthermore, a significant interaction between AST/ALT and triglycerides (TG) was observed (P interaction = 0.026). In conclusion, elevated LFI levels in early pregnancy were strongly associated with an increased risk of GDM, with a positive causal relationship between ALT and GDM. These findings suggest that liver biomarkers, particularly ALT, may serve as useful indicators for early GDM prediction. | Risk factor | GDM |
RF's name
Aspartate Aminotransferase
RF's type
Liver function indicator