| Literature link | GPT Summary | Evidence category | Disease type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25249575 | Obesity-associated insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes, is characterized by chronic inflammation in tissues such as visceral adipose tissue (VAT). In this study, we identify B-1a cells, a subpopulation of B lymphocytes, as novel and important regulators of this inflammatory process. B-1a cells are found to be reduced in frequency in obese high-fat diet (HFD)-fed mice, and interleukin-10 (IL-10) reporter mice show a marked reduction in anti-inflammatory IL-10 production by B cells in vivo during obesity. Within VAT, B-1a cells are the dominant producers of B cell-derived IL-10, contributing nearly half of the expressed IL-10 in vivo. Adoptive transfer of B-1a cells into HFD-fed B cell-deficient mice results in significant improvements in insulin resistance and glucose tolerance, mediated through IL-10 and polyclonal IgM-dependent mechanisms, while the transfer of B-2 cells exacerbates metabolic disease. Additionally, genetic knockdown of B cell-activating factor (BAFF) or treatment with a B-2 cell-depleting, B-1a cell-sparing anti-BAFF antibody attenuates insulin resistance in HFD-fed mice. These findings establish B-1a cells as key immune regulators that maintain metabolic homeostasis, suggesting that manipulating these cells could provide a potential therapeutic strategy for insulin resistance. | Mechanism | Insulin resistance |
RF's name
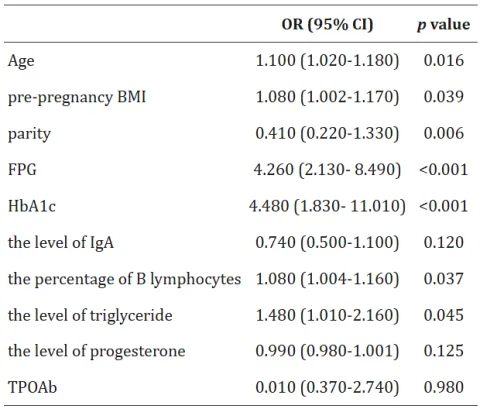
Percentage of B lymphocytes
RF's type
Complete blood count