| Literature link | GPT Summary | Evidence category | Disease type |
|---|---|---|---|
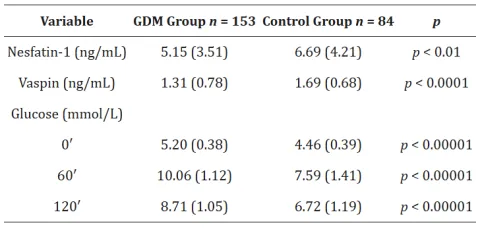
| 30621139 | This study investigated the potential roles of serum nesfatin-1 and vaspin levels as biomarkers for the prediction and early diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). Serum concentrations of nesfatin-1 and vaspin were measured in 153 women with GDM and 84 women with uncomplicated pregnancies using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The results showed that circulating levels of nesfatin-1 and vaspin were significantly lower in women with GDM compared to the control group. Moreover, nesfatin-1 levels were negatively correlated with vaspin levels. These findings suggest that nesfatin-1 and vaspin could serve as potential novel biomarkers for GDM risk assessment and early diagnosis. However, further research is required to understand their influence on glucose metabolism during the early stages of GDM. | Risk factor | GDM |
| 22688332 | This study investigates the role of nesfatin-1, a peptide derived from nucleobindin 2, in glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity through central signaling mechanisms. By infusing nesfatin-1 into the third cerebral ventricle of high-fat diet (HFD)-fed rats, the researchers assessed its impact on glucose metabolism using euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamping. The infusion of nesfatin-1 significantly reduced hepatic glucose production (HGP) and promoted muscle glucose uptake. These effects were accompanied by a decrease in the expression and activity of the gluconeogenic enzyme PEPCK in both standard and HFD-fed rats. Additionally, nesfatin-1 infusion activated the insulin receptor (InsR)/insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1)/AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)/Akt kinase (Akt)/target of rapamycin complex (TORC) 2 signaling pathway and increased Fos immunoreactivity in hypothalamic nuclei involved in glucose regulation. These findings reveal a novel mechanism through which hypothalamic nesfatin-1 modulates glucose homeostasis by enhancing insulin sensitivity and reducing gluconeogenesis, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic target for metabolic disorders. | Mechanism | Insulin resistance |
| KEGG pathway |
|---|
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, Insulin secretion, Type II diabetes mellitus |
RF's name
nesfatin-1
RF's type
Satiety factor