| Literature link | GPT Summary | Evidence category | Disease type |
|---|---|---|---|
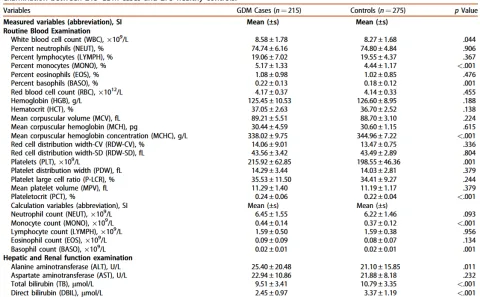
| 32762275 | This study aimed to develop a risk prediction model for gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) within the first 19 weeks of pregnancy using hepatic, renal, and coagulation function markers. A case-control cohort of 490 pregnant women, including 215 GDM cases and 275 controls, was analyzed for 43 blood examination indices. Machine learning models, including support vector machine (SVM) and light gradient boosting machine (LightGBM), were utilized to identify potential biomarkers and construct predictive models. Results showed that prothrombin time (PAT-PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (PAT-APTT) effectively predicted GDM with an AUC of 94.2%, sensitivity of 88.3%, and specificity of 99.47%. Using hepatic and renal function indices, a combination of direct bilirubin (DBIL) and fasting plasma glucose (FPG) achieved an AUC of 91.0% with sensitivity of 82.6% and specificity of 90.0%. Notably, PAT-PT and PAT-APTT were negatively correlated with GDM risk, while FPG was positively correlated. These findings suggest that PAT-PT and PAT-APTT are novel biomarkers for early GDM prediction, and an integrated 19-week prediction model may enable earlier identification and intervention to improve maternal and fetal outcomes. | Risk factor | GDM |
| KEGG pathway |
|---|
| Porphyrin metabolism, Bile secretion |
RF's name
Direct Bilirubin
RF's type
Liver and bile function indicator