| Literature link | GPT Summary | Evidence category | Disease type |
|---|---|---|---|
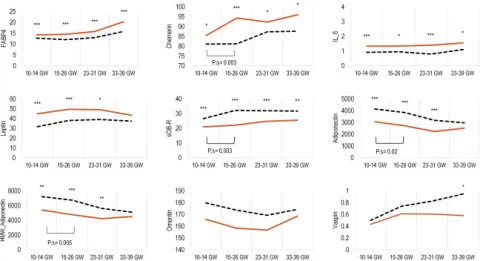
| 32747382 | This study investigated the association between a panel of adipokines in early and mid-pregnancy and the risk of developing gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) in the NICHD Fetal Growth Studies-Singletons cohort. Among 107 GDM cases and 214 non-GDM controls, significant differences in the trajectories of chemerin, sOB-R, adiponectin, and HMW-adiponectin levels were observed from gestational weeks (GWs) 10-14 to 15-26. FABP4, chemerin, IL-6, and leptin were positively associated with increased GDM risk, while adiponectin and sOB-R were inversely associated with GDM risk. For example, at GWs 10-14, the odds ratio (OR) for GDM comparing the highest versus lowest quartile of FABP4 was 3.79, while for adiponectin it was 0.14. Including these adipokines in predictive models improved the area under the curve (AUC) for GDM prediction from 0.71 to 0.77. These findings highlight the potential role of adipokines, particularly FABP4 and chemerin, in the early pathogenesis of GDM and suggest their utility for improving early GDM risk prediction. | Risk factor | GDM |
RF's name
Soluble Leptin Receptor
RF's type
protein