| Literature link | GPT Summary | Evidence category | Disease type |
|---|---|---|---|
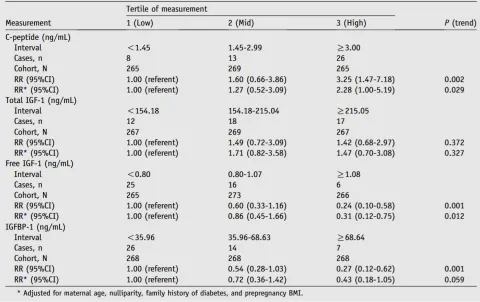
| 16260212 | This study aimed to investigate the relationship between circulating concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), IGF binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1), and C-peptide in early pregnancy with the development of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). The study included 804 women, and maternal plasma samples were collected at 13 weeks of gestation to measure IGF-1, IGFBP-1, and C-peptide. The results showed that higher levels of free IGF-1 and IGFBP-1 were inversely associated with GDM risk, whereas higher C-peptide levels were positively associated with GDM risk. Specifically, women with free IGF-1 levels ≥ 1.08 ng/mL had a 69% reduced risk of GDM compared to those with levels < 0.80 ng/mL. Similarly, women with IGFBP-1 levels ≥ 68.64 ng/mL had a 57% reduced risk of GDM, although the result was not statistically significant. Conversely, women with C-peptide levels ≥ 3.00 ng/mL had a 2.28-fold increased risk of developing GDM compared to those with lower levels. These findings suggest that both IGF-1 and IGFBP-1 may play protective roles against GDM, while elevated C-peptide levels could increase the risk. |
Risk factor |
GDM |
| 34860303 | G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are crucial players in various human pathophysiological processes and represent potential targets for extending lifespan and healthspan. This study examines the role of specific GPCRs in modulating longevity in both animal and human models, focusing on the molecular mechanisms involved. Key pathways identified include those that mimic dietary restriction, insulin signaling, AMPK and TOR pathways, as well as mechanisms that regulate oxidative balance and inflammation. The findings suggest that modulating GPCR activity through agonists or antagonists could offer therapeutic strategies to enhance lifespan and promote health, depending on the receptor’s effect |
Mechanism |
Insulin resistance |
| 37834331 | Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) is a key peptide growth factor involved in growth, development, and metabolism, primarily exerting its effects through the IGF1 receptor (IGF1R), a transmembrane protein structurally related to the insulin receptor (InsR). IGF1 signaling is tightly regulated by IGF-binding proteins (IGFBPs), which modulate its bioavailability in circulation. Mechanistically, IGF1R activation triggers the MAPK and PI3K signaling pathways, promoting cell proliferation and survival. Recent findings indicate that IGF1R can translocate to the nucleus, where it functions as a transcriptional activator, with potential interactions with MAPK signaling. This emerging paradigm expands the role of IGF1R beyond classical signaling, highlighting its importance in oncogenesis. Given its widespread expression in cancer and its potent anti-apoptotic functions, IGF1R represents a promising molecular target for cancer therapy. | Mechanism | Insulin resistance |
RF's name
Insulin-like Growth Factor 1
RF's type
protein