| Literature link | GPT Summary | Evidence category | Disease type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 32937245 | This study aimed to develop a first trimester prediction model for gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) by using obesity, placental, and inflammatory biomarkers. The model incorporated maternal body mass index (BMI), insulin levels, uterine artery pulsatility index (UtA-PI), soluble CD163 (sCD163), pregnancy-associated plasma protein A (PAPP-A), placental protein 13 (PP13), and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα). For obese women, the combination of high BMI, insulin, sCD163, and TNFα yielded a prediction model with an AUC of 0.95 and 89% detection at 10% false positive rate (FPR). In non-obese women, sCD163, TNFα, PP13, and PAPP-A combined gave an AUC of 0.94 with 83% detection at 10% FPR. This model demonstrates promise for early prediction of GDM but requires further validation. |
Risk factor |
GDM |
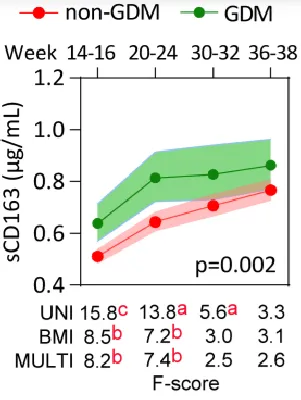
| 30548982 | This study investigated the dysregulation of adipokines and monocyte/macrophage markers in gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) and their potential for early detection. It found that sCD163 levels were elevated and adiponectin levels decreased in women with GDM, independent of BMI. Additionally, markers like leptin and adiponectin were associated with glucose metabolism throughout pregnancy. While sCD163 showed modest predictive value for GDM when combined with fasting glucose, no single marker provided clinically useful early detection on its own. The study suggests that monocyte/macrophage activation might play a crucial role in the early development of GDM. | Risk factor | GDM |
RF's name
Soluble CD163 antigen